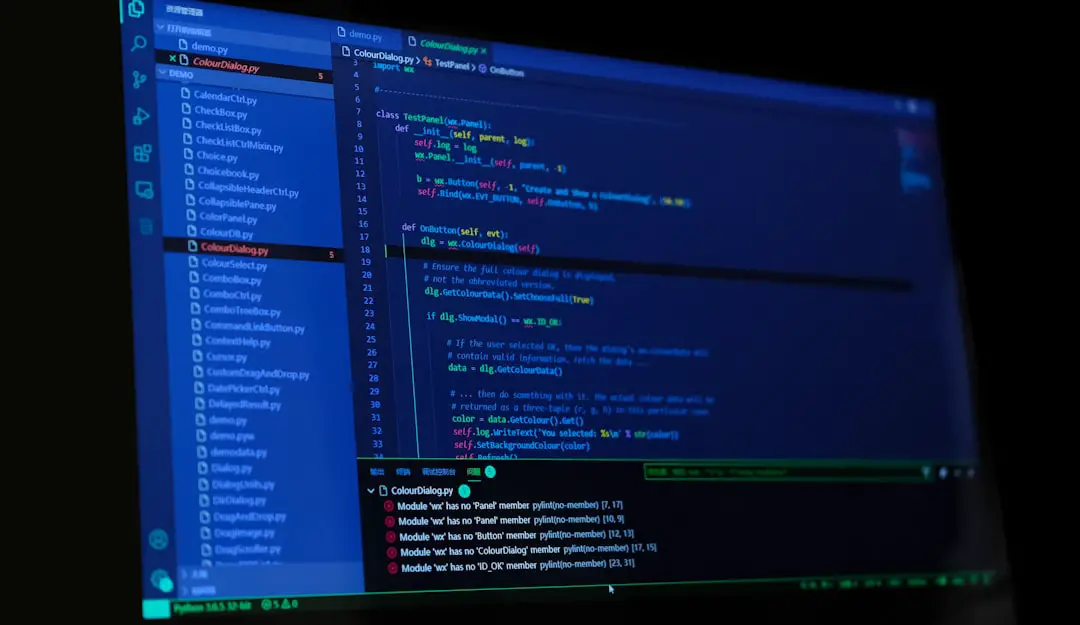
The “Failed to Auto Label – Could Not Complete” error can be a source of frustration for digital content creators, machine learning practitioners, and data labeling professionals. This error typically occurs during the auto labeling process in AI training workflows, data annotation software, or image processing tools when the system is unable to proceed with automatic labeling due to various factors. Understanding the causes of this error and applying the correct methods to resolve it is crucial, especially when working with time-sensitive AI or machine learning projects.
This guide will walk users through common causes, practical solutions, and preventative measures to address this persistent issue. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just getting started with AI datasets, the insights below can make your process smoother and more efficient.
Common Causes of the “Failed to Auto Label – Could Not Complete” Error
The error can arise for several reasons. Understanding these common causes will help narrow down troubleshooting quickly:
- Corrupted or incompatible files: Input data (such as images, videos, or documents) may be corrupted or in unsupported formats.
- Insufficient resources: Auto labeling can be memory-intensive. If the system lacks RAM, GPU processing power, or disk space, it may fail to complete the task.
- Faulty labeling model: The AI model or algorithm used for labeling could be outdated, improperly configured, or incompatible with the dataset.
- Incorrect annotation configuration: Improper label schemas, categories, or template settings may cause the auto labeling system to crash or halt.
- Software bugs: Internal bugs or version mismatches in data annotation tools could lead to operational errors.

Step-By-Step Fixes to Resolve the Error
Once you’ve identified potential root causes, follow these actionable steps to resolve the issue efficiently:
Step 1: Verify the Integrity of Your Data
- Double-check all imported files. Corrupted media or unsupported formats will often cause auto labeling to collapse.
- Convert files to standard formats (e.g., .jpg, .png, .mp4) if necessary.
- Try loading a subset of your dataset to isolate the problem file.
Step 2: Check System Requirements
- Ensure your machine meets the minimum hardware requirements recommended by your labeling tool.
- If possible, monitor system performance to detect spikes in memory or CPU usage during auto labeling attempts.
- Close background applications to free up resources.
Step 3: Update or Reconfigure the Annotation Tool
- Update to the latest version of your data annotation software to benefit from recent bug fixes and better model optimization.
- Review model dependencies and update them to match your software version.
- Reset or reconfigure label schemas if you suspect they’re misaligned with the tool’s requirements.
Step 4: Evaluate the Auto Labeling Model
- If using a custom or pre-trained auto labeling model, make sure it has been properly trained and validated.
- Test the model on a small dataset to assess its functionality.
- Consider switching to a different model (if available) to troubleshoot whether the error is model-specific.
Step 5: Enable Debug Logs for Clarity
- Most professional annotation tools offer debugging or log-output features.
- Enable these logging options to receive detailed system reports.
- Use the logs to identify where in the process the tool fails, which can indicate faulty files, missing dependencies, or misconfigurations.
Step 6: Evaluate Software Permissions
- Especially in enterprise environments, software might not have permission to write to storage directories or access certain files.
- Ensure that user permissions for the tool and its output directories are configured correctly.
Preventing Future Auto Labeling Failures
After successfully fixing the error, implementing preventive strategies will help safeguard your workflow from similar disruptions:
- Standardize file naming: Avoid using special characters or extremely long filenames, which can cause parsing issues.
- Backup configurations: Regularly export and save your labeling configurations and model presets.
- Use clean datasets: Always conduct a dataset quality check before auto labeling begins.
- Train and validate models periodically: Enhancing your auto labeling model through updates will improve accuracy and reliability over time.

When to Seek Support
If all attempts fail and you continue to receive the “Failed to Auto Label – Could Not Complete” error, it might be time to seek help:
- Consult the documentation or user manual of the specific tool you are using.
- Explore developer forums: GitHub, Stack Overflow, and product community pages are great resources.
- Reach out to the tool’s technical support team with detailed logs and screenshots for faster resolution.
Final Thoughts
While the “Failed to Auto Label – Could Not Complete” error may seem daunting, most causes can be identified and resolved with systematic diagnostics and best practices. Proper dataset management, keeping tools updated, and using well-configured labeling models can dramatically reduce the chance of error. As auto labeling continues to be a core element in artificial intelligence workflows, mastering these techniques will enhance productivity and streamline model training processes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is auto labeling in machine learning?
A: Auto labeling is the process of automatically labeling data (images, text, video) using AI models, reducing human effort in the data annotation phase of machine learning. -
Q: Can I recover my work after this error appears?
A: Yes, as long as your data and configuration files are intact, your work can usually be recovered after resetting or fixing the issue. -
Q: Does this error mean my model is broken?
A: Not necessarily. The problem may lie with file corruption, configurations, or insufficient system resources. -
Q: What tools commonly face this issue?
A: Tools like Labelbox, CVAT, VGG Image Annotator, and custom-built data annotation tools may experience this error, depending on how auto labeling is implemented. -
Q: Are there alternatives to auto labeling if the error persists?
A: Yes. Manual labeling or semi-automated labeling (combining model and user input) can be used as alternatives until a more robust solution is found.